Coins from a nation that wasn’t: Araucania and Patagonia
By David Bergeron, Curator
D’Antoine de Tounens in a meeting with the Mapuche people of Patagonia. (Wikimedia Commons, Jules Peco?)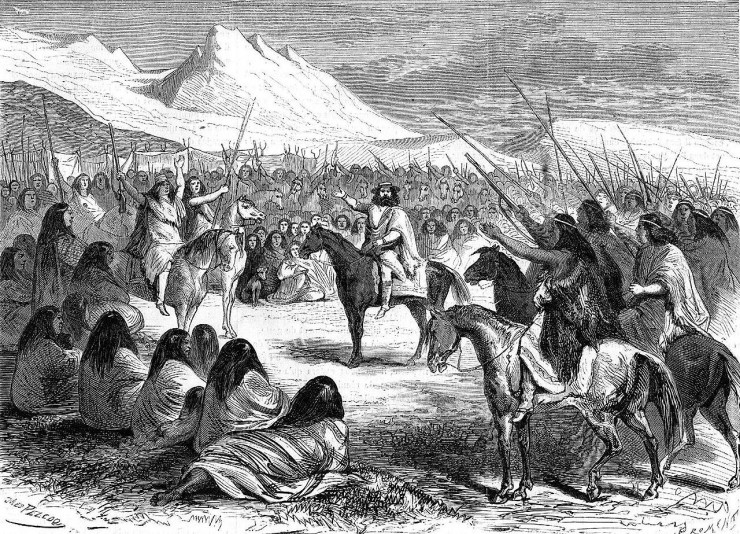
It is not unusual for “micro-nations”— city-states, principalities or minor kingdoms—to produce their own currency. Having a national currency is one way that a fledgling nation can promote its independence—sometimes before there even is a nation. But this coin, from a purely conceptual country in South America, is most intriguing for the history it now represents: the attempt of an indigenous people to establish their own nation in the face of colonization. Even more intriguing, what’s stamped on the coin implies this imaginary nation had already been colonized–by France.
Patagonia from the survey by the British ships Adventure and Beagle. (Wikimedia Commons, John Arrowsmith, 1842)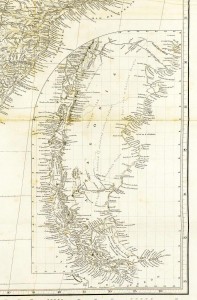
In the middle of the 19th century, a French lawyer and adventurer named d’Antoine de Tounens became fascinated by the Mapuche people of the Patagonia region of South America. The Mapuche were struggling to protect their ancestral lands, their identity and their culture from colonial expansion by the governments of Chile and Argentina. De Tounens went to Chile in 1858 to meet the Mapuche, whom he admired for what he regarded as their heroic resistance, and took up their campaign for self‑determination and sovereignty. In co-operation with their leaders, de Tounens drafted a constitution for “Araucania and Patagonia”, a region located in the southern half of modern Chile and Argentina. They declared the district a kingdom and de Tounens was named as its first monarch. The Chilean government arrested him in 1862, put him on trial and declared him insane. Narrowly avoiding execution, de Tounens was deported to France.
The National Currency Collection possesses three 2-centavo coins minted for Araucania and Patagonia in 1874. What is so curious about these coins is that they claim this potential nation for France. The legend on the reverse reads “NOUVELLE FRANCE / DOS / CENTAVOS / 1874". De Tounens appeared to have baptized the nation as part of New France, yet this designation is seen nowhere else but on the coins. The coins don’t originate from South America but by some accounts may have been struck, presumably at de Tounens’ request, in Belgium.
De Tounens intended to take the coins back with him to Patagonia to help re-establish his kingdom. Although he returned and failed on several occasions, a number of countries did choose to recognize his fledgling state. But it was not to be. In 1878, Orélie-Antoine de Tounens (as his magisterial name was) died in France as the exiled King of Araucania and Patagonia. A successor to the office of Royal Highness to the Crown of Araucania and Patagonia (in exile) still lives in France today–Prince Antoine IV.
The Museum Blog
New Acquisitions—2022 Edition
It’s a new year—the perfect time to look back at some notable artifacts the Museum added to the National Currency collection from 2022. Each object has a unique story to tell about Canada’s monetary and economic history.
Money: it’s a question of trust
By: Graham Iddon
The dollars and cents we use wouldn’t be worth anything to anybody if we didn’t have confidence in it. No matter if it’s gold or digits on a hard drive, public trust is the secret ingredient in a successful currency.
The day Winnipeg was invaded
By: David Bergeron
People on the street were randomly stopped and searched, and some were even arrested and imprisoned in an internment camp. Even German marks replaced Canadian currency in circulation—in the form of If Day propaganda notes.
Positive notes
By: Krista Broeckx
The imagery on the Bank of Canada’s 1935 note series depicts the country’s rich industrial history.
Army bills: Funding the War of 1812
In 1812, British North America had no banks and little currency. With the prospect of war drying up supplies of coins, the government of Lower Canada decided to issue legal tender notes called “army bills” to pay for troops and supplies.
Between tradition and technology
By: Graham Iddon
What was proposed was a complete about-face from the philosophy behind recent security printing. If photocopiers could easily deal with the colours and designs of the current series, then the next series should be bold and simple.
Teaching the green economy
By: Adam Young
From windmills and solar panels to electric cars, signs of the green economy are all around us. Check out our resources for how to teach about the green economy.









