Coins from a nation that wasn’t: Araucania and Patagonia
By David Bergeron, Curator
D’Antoine de Tounens in a meeting with the Mapuche people of Patagonia. (Wikimedia Commons, Jules Peco?)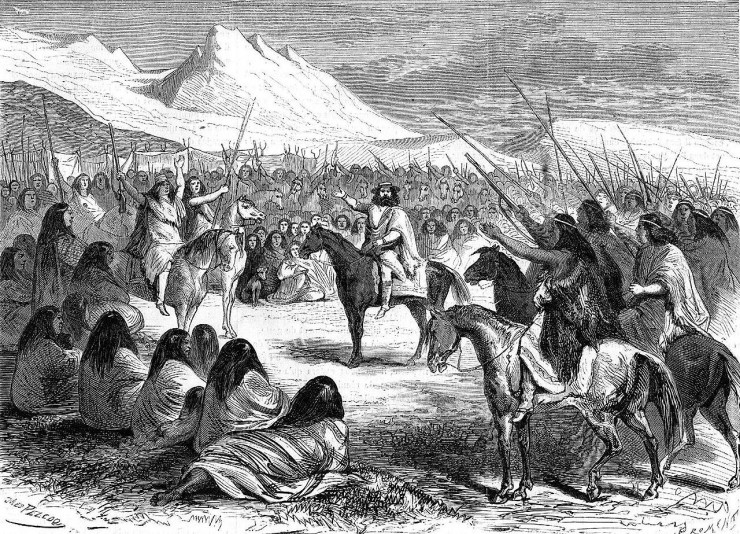
It is not unusual for “micro-nations”— city-states, principalities or minor kingdoms—to produce their own currency. Having a national currency is one way that a fledgling nation can promote its independence—sometimes before there even is a nation. But this coin, from a purely conceptual country in South America, is most intriguing for the history it now represents: the attempt of an indigenous people to establish their own nation in the face of colonization. Even more intriguing, what’s stamped on the coin implies this imaginary nation had already been colonized–by France.
Patagonia from the survey by the British ships Adventure and Beagle. (Wikimedia Commons, John Arrowsmith, 1842)
In the middle of the 19th century, a French lawyer and adventurer named d’Antoine de Tounens became fascinated by the Mapuche people of the Patagonia region of South America. The Mapuche were struggling to protect their ancestral lands, their identity and their culture from colonial expansion by the governments of Chile and Argentina. De Tounens went to Chile in 1858 to meet the Mapuche, whom he admired for what he regarded as their heroic resistance, and took up their campaign for self‑determination and sovereignty. In co-operation with their leaders, de Tounens drafted a constitution for “Araucania and Patagonia”, a region located in the southern half of modern Chile and Argentina. They declared the district a kingdom and de Tounens was named as its first monarch. The Chilean government arrested him in 1862, put him on trial and declared him insane. Narrowly avoiding execution, de Tounens was deported to France.
The National Currency Collection possesses three 2-centavo coins minted for Araucania and Patagonia in 1874. What is so curious about these coins is that they claim this potential nation for France. The legend on the reverse reads “NOUVELLE FRANCE / DOS / CENTAVOS / 1874". De Tounens appeared to have baptized the nation as part of New France, yet this designation is seen nowhere else but on the coins. The coins don’t originate from South America but by some accounts may have been struck, presumably at de Tounens’ request, in Belgium.
De Tounens intended to take the coins back with him to Patagonia to help re-establish his kingdom. Although he returned and failed on several occasions, a number of countries did choose to recognize his fledgling state. But it was not to be. In 1878, Orélie-Antoine de Tounens (as his magisterial name was) died in France as the exiled King of Araucania and Patagonia. A successor to the office of Royal Highness to the Crown of Araucania and Patagonia (in exile) still lives in France today–Prince Antoine IV.
The Museum Blog
What’s Up Next for 2019?
By: Graham Iddon
Instead of bragging about our visitor statistics and the popularity our programming (both great!), we’ll talk about what’s coming up for early 2019.
Boer War Siege Money
By: Graham Iddon
As in any siege, Mafeking quickly began to run short of most things, not the least of which was cash.
Unpacking the Collection 11
By: David Bergeron
The size of the 1-cent coin was reduced to save on the cost of copper. At the same time, there were proposals to mint Canadian coins out of cheap and abundant nickel.
A Good Deal
By: David Bergeron
In Canada playing cards were used as form of emergency money at a time when the colony constantly suffered from a shortage gold and silver coins.
Unpacking the Collection 10
By: David Bergeron
During the first international assembly of the Ligo in 1946, a decision was made to introduce a common world currency with an internationally stable value.
Unpacking the Collection 9
By: Raewyn Passmore
Wars have been fought to control its trade and gifts of it have been made to ensure peace. It has even been used as currency.









